Study Bay Coursework Assignment Writing Help
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The report focuses upon the constituents of project success and provides key recommendations to enhance the company’s policy manual and understanding. The constituents are:
- Timescale
- Cost
- Quality
- Health and Safety
- Legacy
Case studies examining projects which are established as being excessively flawed in one or more area feature:
- The Boston ‘big dig’, USA (timescale, cost, quality, safety)
- Qatar 2022 World Cup (safety, legacy, quality)
- Sydney Opera House (timescale, cost)
In contrast, the London 2012 Olympic project is regarded as a major success. This expansive project was delivered safely on time, on budget and boasts a positive legacy. Failures common to the flawed projects are compared to the success of the Olympics.
These company qualities constitute project management success:
- achieving ambitious performance targets
- developing partnerships
- Having a trained, integrated, experienced and motivated workforce
- placing value delivered over costs saved
THE CONSTITUENTS OF SUCCESS
Project management is a continuously evolving discipline. There is no golden formula to ensure perfect success (Smith, 2008). However, understanding gained through experience, investment in training and development of targets helps realise a project as successfully as possible. The constituents of success may be identified as:
- Timescale.
A successful company adheres to defined objectives, plans effectively, anticipates problems and delivers a project to the client by an agreed deadline.
- Finance.
This is not just about keeping costs low and within a defined budget, but about delivering the best value. Waste should be minimised and labour efficiency maximised. Margins are traditionally low in the industry (Egan, 1998): a successful company does not merely survive but makes a good enough profit to:
- Continue delivering the best value for clients and stakeholders
- Attract long term shareholders
- Invest in training, research and product development.
- Be honest and realistic about budgets
- Quality.
There should be no building defects and through value management, client expectations should not only be met but exceeded. Through quality, a successful company retains and grows their client base and develops partnering arrangements. Partnerships with major clients reduce cost and timescales (Egan, 1998).
- Health and Safety.
A successful project ensures a paucity of injuries and avoids fatalities.
- Legacy.
A successful project leaves an appropriate, lasting imprint in the following ways:
- Political – promoting infrastructure and industry improvement.
- Economic – generating income for the area.
- Environmental – sustainability, adhering to low carbon construction.
- Cultural – benefitting all stakeholders.
- Technical – pushing the boundaries of achievement.
Ideally succeeding on all levels, projects may instead succeed in one or more area but fail excessively in other areas. Three cases deemed overall failures are examined.
FAILURE CASE STUDIES
THE ‘BIG DIG’, BOSTON, USA

Figure 1 – The ‘Big Dig’ or Central Artery/Tunnel Project (Geotimes, 2002)
The ‘Big Dig’, launched in 1991, was the most expensive construction scheme in U.S. history designed to replace an outdated highway costing the economy $500 m/year (Silverman, 2015).
The project was originally estimated at $2.6 billion due for completion in 1998 (National Academy of Engineering, 2003). However, delays pushed the project completion date to 2007 with cost overruns of $12.2 billion (Silverman, 2015).
There were numerous reasons for the project delays:
- Tunnel leaks caused by lack of due diligence
- Program delays due to numerous revisions of the signature cable stayed bridge
- Change of management and communication issues
- Failure to manage client and stakeholder involvement
- Challenges of undertaking construction alongside daily public use
Additionally, a tragedy occurred when ceiling panels in a tunnel collapsed, causing a fatality and resulting in extensive litigation for management. Federal investigation blamed inadequate materials and the project’s escalating budget (LeBlanc, 2007).
The excessive failures of the project led to extensive Assessment. Figure 2 shows the changing total project cost. Inflation contributed heavily – approximately $6.5 billion. However, the true impact was difficult to assess due to the dynamic interplay of scope, schedule and construction costs. Mitigation costs were inadequately quantified (National Academy of Engineering, 2003).
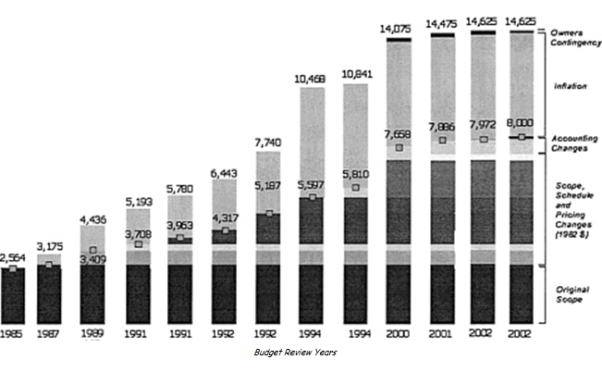
Figure 2 – Cost History and Scope Evolution, in millions of dollars (Data from Edwards, 2002)
2022 WORLD CUP, QATAR
Figure 3 – Stadium construction site (Bhatia, 2014)
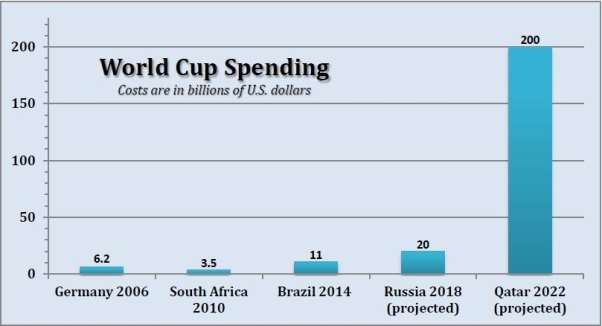
The 2022 World Cup in Qatar is another prominent example of management failure. It remains to be seen whether the project will finish on time and on budget, although the figure reported by Deloitte is an excessive $200 billion USD (Figure 4) (Deloitte, 2013).

However, regardless of final performance in these regards, the project will be remembered as an appalling failure in safe and responsible construction. Reports have emerged exposing unethical (and in some cases, illegal) practises on the part of contractors responsible for the various sites and developments.
Despite the colossal spending involved in the project, the cost of construction work has been minimised through cheap migrant labour subjected to poor working conditions and minimal pay. Workers’ payslips reveal that some labourers were paid as little as £4.90 a day, or 45p an hour. In other cases, pay has been withheld for up to one year (Booth and Pattison, 2014).
Beyond financial exploitation, there has been disregard from contractors regarding safety on-site: controls are often lax and additionally, labourers are required to work in extreme temperatures for long hours. Both of these factors combined resulted in a reported death toll of over one per day for workers in 2014 (Gibson and Pattison, 2014). Figure 5 illustrates the death toll in comparison with equivalent sporting events.

Figure 5 – Construction deaths in recent sporting events (London Loves Business, 2014)
It should be noted that this performance can be attributed primarily to the contractors managing the projects – an international law firm’s report confirmed that “it appears clear to us that the legislation is in place to ensure migrant workers’ wages are paid and to preclude unauthorised deductions. It is, therefore, an issue of the proper monitoring and enforcement of such legislation.” The same conclusion was also expressed regarding worker safety considerations (DLA Piper, 2014).
Regardless of deadlines or commercial performance, a key managerial role must be to ensure a safe, ethically run site. For this reason the construction of Qatar 2022 will always be considered a failure.
3.3 SYDNEY OPERA HOUSE
Known globally as the symbol for Australia, Sydney Opera House is arguably one of the world’s most breath-taking structures, floating effortlessly atop the Sydney Harbour. However, the task of realising the project was far from effortless.

Figure 6 – Sydney Opera House (SOH) (Enochlau, 2006)
In 1957, architect Jørn Utzon won the competition initiated by the New South Wales government for the building. Construction started in 1959 with Utzon as project manager.
The first failure stemmed from biased judgement tending to architectural form rather than feasibility. The judging panel also failed to evaluate how much experience the competition entrants had with large-scale design projects.
The incomplete, untested structural strategy proposed to achieve the complex roof design was the second failure; the project started without a full set of completed drawings (MIT, 2011). This was one of the first major projects to be designed using CAD software, thus imposing challenges in itself.
Furthermore, there was no clear program, resulting in major design changes being made on a daily basis during construction. These changes included the demolition and reconstruction of parts of the structure and consequently the budget soared to an unprecedented level.
Stakeholders began to get involved and demanded alterations be made for financial reasons. For example, the Australian Broadcasting Commission wanted the proposed larger opera hall to be converted to a concert hall because to increase revenue through larger audiences (MIT, 2011).

Figure 7 – SOH under construction (Martin, 2012)
In 1966 Utzon resigned as project manager, taking the majority of the designs with him. The new management subsequently struggled to replicate them which had significant cost and program implications.
The project took 14 years to complete, which was originally planned for 4 years. The total cost amounted to $102 million AUSD; the initial estimate was $7 million (Martin, 2012). The scale and complexity of the project was unprecedented and the original cost estimate was highly unrealistic.
A SUCCESS STORY: LONDON OLYMPIC GAMES 2012
The London 2012 Olympics was undoubtedly a management success. This can be attributed to two key factors – ambitious targets and foresight in planning.

Figure 8 – Queen Elizabeth 11 Olympic Park, London (Inhabitat, 2010)
The Olympic Design Authority (ODA) had clearly defined targets concerning environment and sustainability, health & safety and design legacy.
PICTURE
The ODA began planning the Olympic bid and brief well in advance of construction. They utilised the knowledge and experience of specialist government departments (e.g. Health and Safety Executive) concerning:
- The commissioning of studies to identify contractors with relevant experience
- Setting targets for each phase
- Monitoring and developing partnerships with contractors
- On site health and safety management (HSE involvement)
Despite a multitude of challenges arising from the enormous scale, the project succeeded on many levels:
- Delivered on time – final works completed in September 2011.
- Exemplary health and safety record – the plan was to set a new standard in construction, to research & educate the industry to develop a health and safety conscious and proactive culture. This was achieved emphatically; there were no work related fatalities on the whole of the construction programme. Injury frequency rate as reported by the HSE per 100,000 hours worked was 0.16, well below the industry average of 0.55 (Bolt et al, 2012).
- Legacy – The project provided: re-use of world class sporting facilities, affordable housing to a now prime area, implementation of modern infrastructure and a massive urban regeneration programme.
- Cost – The original cost of the games in its entirety was advertised at around the £2.4 billion mark. This was revised to £9.3 billion in 2007 (DCMS 2012). Despite being initially over budget, there was openness and transparency concerning financing. This resulted in a revised, realistic budget which delivered a successful venue for the games.
COMMON FAILURES AND COMPARISON WITH SUCCESS
Considering the constituents of success in section 2, table 5.1 compares common themes found within the failures to the success of London 2012.
Table 5.1: Comparing common failure themes with success.
|
Criterion |
Failure |
Success |
|
Timescale |
Absence of planning, lack of communication and unrealistic ambitions. |
Early-stage planning, integrated teams and realistic goals. |
|
Finance |
Lack of accuracy and honesty with the budget. |
Openness and transparency with the budget. |
|
Quality |
Substandard materials, undelivered value and inexperienced contractors. |
Good quality of build, value delivered to the client and stakeholders. |
|
Health and Safety |
Fatalities, injuries, no state concern over worker welfare and exploitation. |
Safety as a priority, no fatalities, injury rate well below industry average. |
|
Legacy |
Litigation problems, all stakeholders not benefitting and negative economic impact. |
Re-usable facilities, urban regeneration, cultural pride, beneficial to community and economic gains. |
It is clear that a project may be deemed a success if the above criteria are achieved with the exception of sticking rigidly to an original budget. Ultimately, the British Government was correct in spending more to entirely achieve the other four criteria.
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
This report concludes that having control and command of the five areas outlined in sections 2 and 5 constitutes success. If a project is a technical success but fails on other levels, then it may be deemed an overall failure. Equally, saving money does not equate to success or delivering the best value for stakeholders and spending money does not guarantee safety.
The policy manual should therefore state that the company:
- Establishes and adheres to a system of clear performance targets.
- Allowing Assessment of quality and performance.
- Pursues a culture of establishing partnering relationships with clients offering repeat business.
- Improving efficiency.
- Decreasing the need for tendering and contracts (Egan, 1998).
- Employs an integrated, trained, safe and motivated workforce.
- Sharing and pooling experience across disciplines.
- Working together on numerous projects.
- Avoiding fatalities and major injuries.
- Considers finance by value delivered rather than money saved.
- Exuding financial honesty and transparency.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Bolt, H. Haslam, R. Gibb, A. Waterson, P., (2012). Pre-conditioning for success. Loughborough: HSE, (RR955).
Booth, R., Pattison, P. 2014. Qatar World Cup stadium workers earn as little as 45p an hour [online]. Doha: The Guardian. Available from: http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/jul/29/qatar-world-cup-stadium-workers-earn-45p-hour [Accessed 21/02/15]
Booth, R., Pattison, P. 2014. Qatar World Cup: migrants wait a year to be paid for building offices [online]. Doha: The Guardian. Available from: http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/jul/28/qatar-world-cup-migrants-not-paid-building-office [Accessed 21/02/15]
Bust, P. (2011). Learning legacy. Loughborough: Loughborough University, (ODA 2011/269).
Deloitte, 2013. Insight into the Qatar construction market and opportunities for real estate developers. Middle East: Deloitte Corporate Finance Limited.
Department of Culture, Media and Sport. (2010). November London 2012 Olympic and Paralympic budget report published – Anticipated final cost down £29m. Gov Announcements Online. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/november-london-2012-olympic-and-paralympic-budget-report-published-anticipated-final-cost-down-29m–2 [Accessed 25/02/2015
Department for Culture, Media and Sport, (2012). London 2012 Olympic And Paralympic Games – Quarterly Report. London: DCMS
DLA Piper, 2014. Migrant labour in the construction sector in the state of Qatar. Qatar: DLA Piper UK LLP
Egan, J.,The Construction Task Force. Rethinking Construction. 1998. [online]. Available from: URL http://www.constructingexcellence.org.uk/pdf/rethinking%20construction/rethinking_construction_report.pdf [Accessed 16 February 2015].
http://www.constructingexcellence.org.uk/pdf/rethinking%20construction/rethinking_construction_report.pdf [Accessed 16 February 2015].
Egan, J.,The Strategic Forum for Construction. Accelerating Change. ISBN 1 898671 28 1. Rethinking Construction, Construction Industry Council.
ENOCHLAU. (2006) Sydney Opera House Sails. [Online]. Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sydney_Opera_House_Sails.jpg#filehistory . Wikipedia. [Accessed on: 26th February 2015].
Gibson, O., Pattison, P. 2014. Death toll among Qatar’s 2022 World Cup workers revealed [online]. Kathmandu: The Guardian. Available from: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/dec/23/qatar-nepal-workers-world-cup-2022-death-toll-doha [Accessed 21/02/15]
IRVINE, J. (2013) Why Sydney’s Opera House was the world’s biggest planning disaster. [Online]. Available from: http://www.couriermail.com.au/news/why-sydneys-opera-house-was-the-worlds-biggest-planning-disaster/story-e6freon6-1226744769556 . [Accessed on: 26th February 2015].
LeBlanc, Steve., 2007. On Dec. 31, It’s Official: Boston’s Big Dig Will Be Done [online]. Available from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/12/25/AR2007122500600_3.html [Accessed 13 February 2015].
MARTIN, C. G. O. (2012) The Sidney Opera House construction: A case of project management failure. [Online]. Available from: http://www.eoi.es/blogs/cristinagarcia-ochoa/2012/01/14/the-sidney-opera-house-construction-a-case-of-project-management-failure/ . [Accessed on: 26th February 2015].
MIT. (2011) Project Assessment. [Online]. Available from: file:///C:/Users/staples/Documents/Bath%20University/3rd%20Year/Semester%202/Management%202/The%20Sydney%20Opera%20House.pdf . [Accessed on: 26th February 2015].
National Research Council Committee for Review of the Project Management Practices Employed on the Boston Central Artery/Tunnel (“Big Dig”) Project, National Research Council, National Academy of Engineering., 2003. Completing the “Big Dig”: managing the final stages of Boston’s central artery/tunnel project. National Academies Press, 2003, pp, 1,3,7,8,10,12,14,17.
Silverman, Jacob., 10 Construction Projects That Broke the Bank [online]. Available from: http://science.howstuffworks.com/engineering/structural/10-construction-projects.htm#page=9 [Accessed 13 February 2015]
Smith, N.J., 2008. Engineering Project Management. ISBN: 978-1-4051-6802-1. Blackwell Publishing, Third Edition.
http://www.geotimes.org/oct02/bostonsandgravel.jpg
(Source: W.Edwards, “Project History,” Presentation to the Committee on October 21, 2002)
Qatar World Cup preparation expected to invite deals worth $150bn Bhatia, N. 2014. http://www.bigprojectme.com/news/qatar-world-cup-preparation-expected-to-invite-deals-worth-150bn/
http://www.usnews.com/news/blogs/data-mine/2014/06/24/world-cup-price-tag-multiplies-with-time
Vinter, R
Image Available – http://assets.inhabitat.com/wp-content/blogs.dir/1/files/2010/10/ukolympic-ed01.jpg

