Study Bay Coursework Assignment Writing Help
- Introduction
Hemodynamics is the research of blood movement throughout the physique and forces affecting it, usually measured utilizing numerous strategies which are both invasive or noninvasive. Hemodynamic monitoring is important for making well timed affected person Assessment, prognosis, prognosis, and therapy choices in case of cardiovascular malfunctions and imbalances prompted within the quantity of blood ejected by the center. There are a number of invasive strategies for monitoring blood movement like Thermodilution, Dye dilution and Fick strategies. These strategies are normally confined to hospitals and clinics with individuals having particular abilities carry out, additionally, these strategies are related to issues like infections, hemorrhage, arrhythmia and many others. Impedance Plethysmography strategies which use the adjustments in electrical impedance over physique floor for measurement of adjustments within the tissue volumes can be utilized to review hemodynamics. Impedance Cardiography (ICG) is a noninvasive and versatile methodology of calculating cardiac stroke quantity offering info that’s just like invasive monitoring at low price and threat. Whereas invasive monitoring is completed in pre-operative conditions on sufferers already affected by cardiovascular issues which includes catheter insertion, ICG will be carried out on individuals any time for monitoring hemodynamic parameters that may Help in prognosis of issues occurring in close to future. There are a number of methods of monitoring hemodynamics by means of ICG of which Thoracic Electrical Bioimpedance (TEB) is a primary variant that includes placement of electrodes on the basis of the neck and on the cartilaginous part on the decrease finish of the sternum which isn’t connected to any ribs. The amount of blood movement varies throughout each cardiac cycle virtually periodically. This adjustments the electrical impedance in thorax area . Destructive time by-product of the measured impedance known as impedance cardiogram
. Destructive time by-product of the measured impedance known as impedance cardiogram .
.
Analysis within the subject of Impedance Cardiography began with the research of movement of fluids in physique, particularly in cardiac space utilizing Impedace Plethysmography strategies since 1940s [1Bonjer]. By early 1970s Utilizing ICG for calculation of cardiac parameters like cardiac stroke quantity got here on monitor [2Cooley]. A number of comparative research are achieved within the subject between non-invasive ICG and invasive strategies like Thermodilution which proven promising ends in favour of ICG [3 Nechwatal, 4Denniston].In [5Quesnay] they mentioned the implementation of ICG on topics with coronary heart illnesses and whereas they have been performing train. Outcomes have proven that cardiac parameters measured throughout these checks are dependable and largely correct. With enchancment in know-how in ICG, wearable gadgets or clothes are being designed for facilitating long run recordings and supply consolation to the sufferers or take a look at topics [6JUAN]. For the reason that inception of impedance cardiography there was a rise within the reliability of the method and enchancment in measurement of cardiac parameters [7Greenfield – 13Dilek].
Measurement of ICG requires the themes to put in a supine place with none motion to cancel out the artifacts which are prompted on account of different physique alerts which result in undesirable adjustments of the sign recorded and make the affected person uncomfortable. Presence of those artifacts makes it tough for the individuals studying the alerts and in addition have an effect on the prognosis resulting in outcomes which are inaccurate. These artifacts need to be eliminated earlier than monitoring the alerts to take right choices by means of filtering. Most of those artifacts are non-stationary in nature and can’t be predicted. Artifacts which are distinguished in TEB embody these various with the adjustments that happen in environment like energy line interference which makes bottom line of the unique sign to alter and with the motion of affected person. Some artifacts happen from inside our physique like Respiratory artifact that’s distinguished in ICG .Typically sufferers are required to carry their breath to cancel out this artifact, however it’s proven in [5Quesnay] that this will likely have an effect on the stroke quantity parameter. There are additionally others like Movement artifacts and Electrode artifacts which convey adjustments to the alerts which are undesirable.
Filtering strategies for processing the artifacts are both adaptive or non-adaptive. For the reason that artifacts which are to be processed within the alerts obtained are ever altering in nature, non-adaptive filters which have linear switch capabilities doesn’t present good ends in the method. Whereas time various potentials will be detected utilizing adaptive filtering strategies whose filter specs change at each step. In [14Huang] they used LMS algorithm based mostly adaptive filter for cancellation fo movement artifacts and bought passable outcomes. In [15Allan] Allan et.al used a scaled fourier linear mixed (SFLC) method is proposed for filtering noncorrelated noise in ICG. They’ve succeeded in proving that their proposed methodology might take away noises that aren’t in synchronization with coronary heart fee. In [16Dormer] used SFLC-RLS filter which reveals enchancment in efficiency in comparison with SFLC-LMS filter utilized in [15Allan]. [17Pandey] used LMS based mostly adaptive filtering to take away respiratory artifacts in Impedance cardiogram sign. On this paper we mentioned software of Least Imply Sq. (LMS) algorithm and its variants Normalized LMS (NLMS), Time various step dimension (TVSLMS) Adaptive step dimension (ASLMS) and Constrained stability LMS (CSLMS) in ICG alerts for artifact elimination. Together with these algorithms, signed regressor type of these variants which decreases the variety of computations are additionally used. The artifacts which are thought of on this paper are Energy Line Interference (PLI), Respiratory artifacts, Movement artifacts (MA), Muscle artifacts. Part II describes the filtering strategies which are used on ICG alerts in short. Part III supplies the data on knowledge acquisition utilizing VU-AMS machine. The outcomes and discussions of the strategies used are given in part IV adopted by conclusions.
- Adaptive Filtering Strategies
- LMS
Invented by Widrow and Hoff in 1960, Least imply squares algorithm is a class of adaptive filters that adapt based mostly on present worth of error sign. Enter to the LMS algorithm is a sign that wants filtering and a desired sign as reference, LMS is an iterative method that minimizes the Imply Sq. Error (MSE) between these two alerts. Low complexity is a big function of LMS algorithm which made it as a benchmark for different adaptive filtering algorithms. The method of filtering utilizing LMS includes the next steps,
- Compute the output from the filter utilizing inputs.
- Estimating the error between the output sign and desired sign.
- Altering the faucet weights of the filter in line with the error obtained above and a continuing step dimension.
The above steps are executed iteratively to cut back the error between filter output and desired sign. Filter will probably be of size L, every time L samples from the enter sign will probably be processed at a time in every step till complete samples are processed. Let x(n) be the enter of the filter and d(n) be the reference sign. Enter is taken from a sliding window over the enter. For each step the window slides over required variety of samples. Let y(n) be the output from the filter and w(n) is the weights of the faucets, these weights will be completely different for each faucet. u is the step dimension which is a continuing. LMS algorithm will be summarized within the equations under which are in accordance with the steps above,



For the primary iteration arbitrary faucet weights are assumed and filtering is began. After a number of iterations the weights adapt in accordance with the error sign to present desired sign as output. Step dimension is a fundamental issue that influences weight replace equation. If the step dimension is just too small, the convergence of the sign will probably be too sluggish and filter requires extra reminiscence. If the step dimension is just too excessive, convergence fee will probably be quicker however there will probably be info loss.
- NLMS
The convergence of output in direction of desired sign is dependent upon weight replace equation. Faucet weights which are up to date are immediately proportional to the current inputs. If the longer term inputs to the filter range vastly with the current inputs of the filter, there will probably be a rise within the error sign. To resolve this downside the step dimension in weight replace equation is normalized with squared Euclidian type of enter vector. The burden replace equation of NLMS method is written as,

Right here b is a small fixed added to keep away from difficulties in case of small x(n) values. NLMS methodology can obtain quicker convergence when in comparison with LMS. For the reason that step dimension of those filters doesn’t change a lot, these are thought of as linear filters which give linear output for linear enter.
- CSLMS
This methodology is an enchancment of NLMS algorithm to attain quicker stability situations. Constrained Stability LMS methodology is described by the equations that comply with,



The place 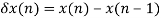 and
and  . A constructive fixed of small worth within the denominator helps stopping issues when worth of x(n) is just too small. Right here the worth of error and enter in weight replace equation not solely rely upon current worth but in addition earlier worth, not like LMS and NLMS the place the dependency of weight replace equation is extra on current values than all of the previous values mixed.
. A constructive fixed of small worth within the denominator helps stopping issues when worth of x(n) is just too small. Right here the worth of error and enter in weight replace equation not solely rely upon current worth but in addition earlier worth, not like LMS and NLMS the place the dependency of weight replace equation is extra on current values than all of the previous values mixed.
- TVSLMS
Step dimension within the weight replace equation decides the convergence fee of the filter. It’s fastened for the filter relying on the enter sign, desired sign and required convergence fee. If the enter sign is various with time in an undetermined approach, it’s tough to set the worth of step dimension. So, time various step dimension methodology of LMS is proposed. The time variance of step dimension is decided by a decaying issue. TVSLMS methodology is described by the next equations,

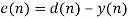

The step dimension at every step will be diversified in line with the next operate,

The place  is the decaying issue and C, a and b are constructive constants that may decide the worth of decaying issue. At every step the decaying issue is multiplied with preliminary step dimension. This methodology can obtain quicker convergence fee in comparison with LMS algorithm with fixed step dimension and in addition can take away the artifacts successfully.
is the decaying issue and C, a and b are constructive constants that may decide the worth of decaying issue. At every step the decaying issue is multiplied with preliminary step dimension. This methodology can obtain quicker convergence fee in comparison with LMS algorithm with fixed step dimension and in addition can take away the artifacts successfully.
- ASLMS
In an surroundings that isn’t stationary a gradient noise is added to the sign. In such case the worth of faucet weights change in random vogue as an alternative of terminating on Weiner answer. To beat this downside Adaptive step dimension algorithm is proposed the place a fourth step is added to the LMS methodology which resembles the load replace equation. Step dimension of the filter is up to date at every step as,
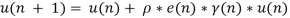
Right here  is a small constructive fixed and y(n) is outlined because the partial by-product of faucet weight vector with respect to step dimension parameter at a pattern or iteration.
is a small constructive fixed and y(n) is outlined because the partial by-product of faucet weight vector with respect to step dimension parameter at a pattern or iteration.

ASLMS attains quicker convergence fee because the step dimension of subsequent iteration is dependent upon the enter and error at present iteration, not like TVSLMS algorithm the place step dimension of current iteration is dependent upon the preliminary step dimension.
- Signed Regressor type
Within the strategies mentioned on this part, from LMS to ASLMS the efficiency of filters elevated with lower in convergence fee however the computational complexity elevated step by step. This may lead to delay of achieving desired outcomes. To manage the issue we use signum operate to seek out the polarity of enter sign in weight replace equation [21Eweda]. Through the use of signum operate to enter sign we think about solely the signal of enter sign as proven under,

The signum operate is given as,

The strategies mentioned above of their signed regressor type have barely inferior convergence fee and regular state error. However because the imply sq. error drops the filter hastens with lowered computations.
- Simulation and outcomes
ICG alerts are acquired by means of VU-AMS (Vrije Universiteit Ambulatory Monitoring System) machine below supervision of professional handlers. This machine is used for recording ICG alerts many a instances and offered dependable outputs [18Gonneke- 20Annebet]. Alerts are acquired from 19 topics for a interval of 30 minutes. Digitized alerts are recorded at 360 samples per second. First 4000 samples of every ICG recording are used for simulation.
References
- Bonjer FH, van den Berg JW, Dirken MNJ. The origin of the variations of physique impedance occurring through the cardiac cycle. Circulation. 1952; 6:415-420.
- Cooley WL, The calculation of cardiac stroke quantity from variations in transthoracic electrical impedance. Biomed Eng 1972; 19:316-319.
- Nechwatal W, Bier P, Eversmann A, König E, The noninvasive willpower of cardiac output via impedance cardiography: Comparative analysis with a thermal dilution method. Primary Res Cardiol 1976; 71:542-552.
- Denniston JC, Maher JT, Reeves JT, Cruz JC, Cymerman A, Grover RF, “Measurement of cardiac output by electrical impedance at relaxation and through train”. J Appl Physiol 1976;40:91-95.
- M.C. Du Quesnay, G.J. Stoute, and R.L. Hughson, “Cardiac output in train by impedance cardiography throughout breath holding and regular respiration,” J. Appl. Physiol., vol. 62(1), pp 101-107, 1987.
- Juan Carlos Márquez Ruiz, “Sensor-Primarily based Clothes that Allow the Use of Bioimpedance Know-how: In direction of Personalised Healthcare Monitoring”, Doctoral Thesis, Stockholm, Sweden, January 2013, ISBN 978-91-7501-603-Zero
- Harley A, Greenfield JC Jr. “Willpower of cardiac output in man via impedance plethysmography”, Aerosp Med. 1968 Mar; 39(three): 248-52.
- R.P. Patterson, “Fundamentals of impedance cardiography,” IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Magazine., vol. eight(1), pp 35-38, 1989.
- Main M J World, “Estimation of Cardiac Output by Bioimpedance Cardiography”, J R Military Med Corps 1990; 136: 92-99
- Nancy M. Albert, “Bioimpedance Cardiography Measurements of Cardiac Output and Different Cardiovascular Parameters”, Crit Care Nurs Clin N Am 18 (2006) 195 – 202
- Chintan V Parmar, Divyesh L Prajapati, Pradnya A Gokhale, Hemant B Mehta, Chinmay J Shah, “Examine of cardiac output based mostly on non – invasive impedance plethysmography in wholesome volunteers”, 2: 5 Sep – Oct (2012) 104 – 108.
- E.Pinheiro, O.Postolache, P.Girão, “Contactless Impedance Cardiography Utilizing Embedded Sensors”, Measurement science assessment, Quantity 13, No. three, 2013
- Dilek Cicek Yilmaz, Belgin Buyukakilli, Serkan Gurgul and Ibrahim Rencuzogullari Mersin, “Adaptation of coronary heart to coaching: A comparative research utilizing echocardiography & impedance cardiography in male & feminine athletes”, Indian J Med Res 137, June 2013, pp 1111-1120
- Zhili Huang, Zhenshen Zheng, Yutian Wu, “Monitoring Impedance Cardiography By Adaptive Technique Throughout Exterior Counterpulsation”, IEEE Engineering in Medication and Biology Society. Vol. 13. No. 2, 1991.
- Allan Kardec Barros, Makoto Yoshizawa, and Yoshifumi Yasuda, “Filtering Noncorrelated Noise in Impedance Cardiography”, IEEE Transactions on biomedical engineering, VOL. 42, NO. three, March 1995
- O. Dromer, O. Alata and O. Bernard, “Impedance Cardiography Filtering utilizing Scale Fourier Linear Combiner based mostly on RLS algorithm”, IEEE EMBS, Sep 2009.
- Vinod Okay. Pandey, Prem C. Pandey, “Cancellation of Respiratory Artifact in Impedance Cardiography”, EMBS, 27th Annual Convention, IEEE, 2005.
- Gonneke H. M. Willemsen, Eco J. C. De Geus, Coert H. A. M. Klaver, Lorenz J. P. Van Doornen, Douglas Carroll, “Ambulatory monitoring of the impedance cardiogram”, Psychophys;o/ogy, 33 (1996), 184- 193 . Cambridge College Press.
- Harriëtte Riese, Paul F. C. Groot, Mireille Van Den Berg, Nina H. M. Kupper, Ellis H. B. Magnee, Ellen J. Rohaan “Giant-scale ensemble averaging of ambulatory impedance cardiograms”, Conduct Analysis Strategies, Devices, & Computer systems 2003.
- Annebet D. Goedhart *, Nina Kupper, Gonneke Willemsen, Dorret I. Boomsma, Eco J.C. de Geus, “Temporal stability of ambulatory stroke quantity and cardiac output measured by impedance cardiography”, Organic Psychology 72, Elsevier(2006)
- E. Eweda, “Assessment and design of a signed regressor LMS algorithm for stationary and nonstationary adaptive filtering with correlated Gaussian knowledge,” IEEE Transactions. Circuits Techniques., vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 1367–1374, Nov. 1990.
