Study Bay Coursework Assignment Writing Help
Failure of metals under long run static hundreds
Introduction
Metals are an vital consider virtually each facet of modern life, as such it’s important that designers have enough information of the behaviour of these supplies when subjected to differing kinds of hundreds in a range of environments (Gere and Goodno 2012). In sensible phrases a steel element is designed to resist static and imposed hundreds over the service life of that element, with the designer taking account of the setting during which the steel is positioned and the sort of load, in addition to different components resembling impacts and corrosion, which might have an effect on the efficiency of the fabric. The design may also embrace an element of security to optimise the achievement of the design life in protected method (Bhaduri 2018).
Madia et al.,(2017) means that the failure of a steel depends on the static and imposed hundreds on the fabric over the life of that materials, with Zerbst et al.,(2019) including that roughly 90% of the incidents are on account of fatigue. In lots of instances, such failure is linked to fatigue cracks began by at geometrical defects resembling holes and notches. Failure can be on account of irregularities within the steel such cavities, voids, corrosion pits and inclusions, which are sometimes the foundation trigger of element failure. Forrest (1970) factors out that failure of steel by fatigue is often the end result of hundreds which might be both repeated or diversified, and the place the utmost quantity load that causes failure is considerably decrease than the static breaking load. The very fact is that in service life, many steel buildings and elements are subjected to various hundreds and while the common induced stresses are typically low and don’t lower the static power, failure should happen on account of fatigue. Forrest (1970) subsequently argues that there are a larger quantity of failures in service on account of fatigue than on account of static failure.
Nonetheless Martin and Vladimír (2017) level out that the circumstances assumed within the design stage, might alter over the long run life of the steel, as such it’s important to grasp the potential environmental and operational circumstances which have an effect on each static and dynamic loading on supplies. Panin et al.,(2017) agree, including that it is very important perceive the affect of long run static hundreds on metals as this will have a significant impact on buildings and pipelines over time, citing the instance of long run static loading on metal gasoline pipelines.
The goal of this essay is to discover failure in metals under long run static hundreds, specializing in static loading on alloys. This essay asks how long run static loading can have an effect on the mechanical properties of these supplies. The essay continues with a quick resume of the important thing mechanical properties of metals earlier than discussing research on static loading on alloys.
Mechanical Properties of Metals
Lascoe (1998) maintains that steel buildings may be manufactured and constructed utilizing a range of metals starting from carbon metal to cold-formed metal to chrome steel and aluminium. The stress-strain curves of every of these supplies is completely different, with completely different yield values and post-yield standards, as proven in Determine 1. It’s evident type the above determine, that for instance excessive power metal and chrome steel have a rounded behaviour with no yield plateau evaluate to gentle metal (Ellobody et al.,(014). Macaulay (2012) agrees, stating that some supplies have a well-defined yield stress, exhibiting linear elastic behaviour, previous to plasticity and failure. Nonetheless there are additionally different supplies the place the tip of the elastic behaviour will not be clear-cut. Moreover, time-dependent behaviour within the elastic-plastic area is negligible for metals under static loading, nevertheless behaviour depends on a spread of components together with temperature, which is able to induce creep. The purpose being that structural efficiency of a steel depends on the micro-structure and macro-structure of the fabric, in addition to properties resembling power under static and dynamic loading, hardness and ductility.
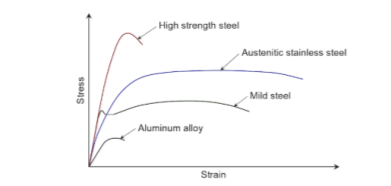
Determine 1. Stress-strain curves of completely different metals (Ellobody et al., 2014, p.four, Determine 1.1)
Hosseini et al.,(2015) level out that in service, a steel construction may be broken by way of a quantity of occasions, and loading situation. As soon as a construction is even partly broken this will have an effect on the vitality absorption, ductility and power of the steel. These load eventualities embrace excessive pressure, static, seismic or thermal loadings. Static loading can happen on account of components resembling basis settlement which may happen over time and which is a typical trigger of harm to the buildings inflicting massive relative displacements in a steel which in the end push the fabric past its yield level. Different types of massive static hundreds embrace lateral floor water stress in relation to non permanent hundreds and bridge piers imposed in restore processes. The purpose being that these hundreds lead to pressure ageing, and it’s submitted that static load- induced pressure ageing can significantly change the mechanical properties of metals resembling metal materials. It’s acknowledged that static hundreds and pressure ageing are thought of on the design stage, each within the manufacturing of the steel and within the selection of the supplies.
Hosseini et al.,(2015) clarify that the place that the pressure getting older impact takes place in steel begins with the motion and formation of linear defects throughout the microstructure of the fabric, known as dislocations. It’s famous that the power of a steel is said to the microstructure of the steel and is basically managed by the stress that’s wanted to make dislocations transfer within the microstructures for appreciable distance. For instance in steels, the presence of carbon and nitrogen are key components in mechanical properties and behavior of the fabric, from which it follows that these substances even have a job in pressure ageing over the long run static loading of metal. In different phrases, the behaviour of the steel in ageing relies on time, with brief time period getting older and long run getting older, the place the latter pertains to the time as a result of of a phenomenon like creep within the materials which takes place in a really very long time. The issues of long run ageing is that it’s tough to foretell the altering circumstances to which a steel is subjected, because the mechanical properties of the fabric may be altered by exterior forces resembling a corrosive setting which makes it tough to state the precise affect of long run static hundreds on failure.
Harris (2014) makes an analogous level, noting that the microstructure of the fabric, has a profound impact on behaviour under long-term static loading. That is in flip is influenced by the tactic manufacturing, and the processes that are used to fabricate the steel. These course of are primarily deformation processes looking for to rework stable supplies from one form into one other. The unique form may by easy resembling a billet or a sheet, which is then plastically deformed utilizing heating processes, tooling and dies, to acquire the specified remaining geometry. As well as the deformation course of usually entails extra operations resembling casting and machining, grinding and warmth treating, to rework the uncooked materials into the completed steel half or element (Nationwide Academy Press 1995). The purpose being that every of these processes impacts the mechanical properties of the steel and in the end the behaviour of that materials under long run static loading (Harris 2014).
While there was important analysis on the impacts of long run static hundreds on typical metals it’s argued that there was little analysis on alloys. But Winzer et al., (2005) level out that alloys play an more and more vital position in trade, with for instance magnesium (Mg) alloys being utilized in a various vary of functions from the car trade (Matta et al., 2018) to medical implants (Witte 2010). For instance Mišović et al., (2016) level out that alloys resembling aluminium alloys would not have an extended custom in engineering nevertheless the elastic and yield limits of these supplies can larger than these of bizarre structural metal components. As well as alloys are usually corrosion resistant and are lighter than typical metals, facilitating transportation and meeting. These supplies additionally exhibit resistance to brittle fracture inside low temperature ranges and have minimal susceptibility to temperature gradient and residual stress. In brief these supplies might be helpful in bettering efficiency under long run static loading. It’s prudent subsequently to discover the impacts of long run static loading on these supplies.
Long Term Static Loading on Alloys
Fedirko, et al., (2014) level out that titanium-based alloys are structural supplies that exhibit excessive physico-mechanical traits, together with particular power and resistance to corrosion in aggressive environments. Nonetheless as with typical metals, a key concern within the power and sturdiness under loading is the tactic of manufacturing. As an illustration a present space of concern is the formation of interstitial impurities in stable options which is brought on by the gasoline saturation across the floor of the steel, which impacts the serviceability of the merchandise. There are a number of proposed options to this downside together with the tactic of floor hardening that may doubtlessly improve the corrosion resistance and to enhance the damage resistance of the steel. Nonetheless some analysis means that this course of will improve the brittleness of the alloy, thereby lowering the power to withstand deformation and fatigue. In brief there is no such thing as a consensus on the optimum methodology for bettering the serviceability of titanium alloys in service of static loading and fatigue, prompting Fedirko, et al., (2014, p.415) to analysis gradient hardening and the way it can doubtlessly affect on the sturdiness of titanium alloys under a range of load circumstances.
The research concerned the use of industrial α titanium alloys together with OT4-1 pseudo-α-alloy (Ti–2.0Al–1.5Mn), PT-7M (Тi–2.5Al–three.0Zr),VT1-Zero (commercially pure titanium), and VT5 (Ti–5Al), all of which had been subjected to a sequence of checks together with cyclic rigidity, rotating bending and pure bending under a uniform load, as proven in Determine 2 (Fedirko, et al., 2014, p.415).
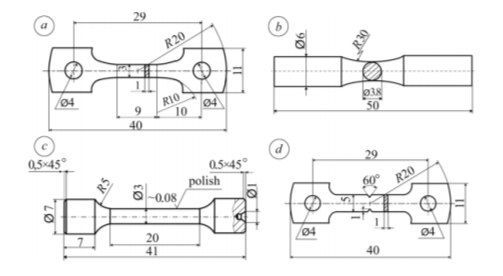
Determine 2. Mechanical check of specimens: (a) cyclic pure bending, (b) rotating bending, (c) cyclic rigidity, (d) and long-term static loading (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.416, Determine 1).
The experiments included utilizing a sequence of specimens with 35-70 µm gasoline saturation layers deep from the subsurface being handled with stable resolution hardening course of inside completely different ranges, Zero%<Okay<100%, utilizing thermo-diffusion saturation. The check outcomes revealed that at a uniform depth within the stiffened zone, Okay (floor hardening stage) rise from 5% as much as 90% thus VT5 and VT1-Zero titanium alloys having elevated fatigue restrict, as proven in Determine three and four (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.417).
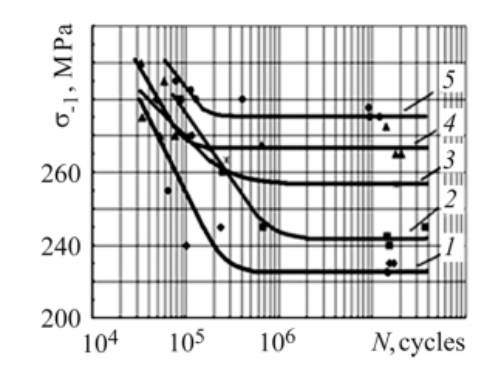
Determine three. How floor hardening impacts the sturdiness of VT1-Zero titanium alloy in rotation bending: (1) Okay = 5%; l = 5 µm; (2) Okay = 25%; (three) Okay = 90%; (four) Okay = 50%; (5) Okay = 70%; (2–5) l ≈ 30 µm (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.418, Determine three).
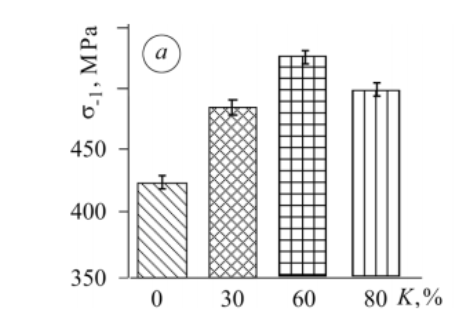
Determine four. How the fatigue restrict of titanium alloys, VT5 and OT4-1 is influenced by the floor hardening. (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.418, Determine 4a).
The identical sample was evident for the OT4-1 alloy as proven in Determine 5
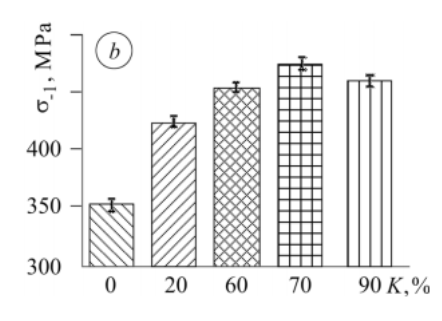
Determine 5. How the fatigue restrict of the alloy is affected by the floor hardening, under the check of rotating bending for 1⋅107 cycles (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.418, Determine 4b).
The research discovered that the best improve of the fatigue restrict for the VT1-Zero alloy was discovered at Okay = 70%, l ≈ 30 µm and for the VT5 alloy at Okay = 60%, l ≈ 30 µm and for the OT4-1 alloy at Okay = 70%, l ≈ 45 µm (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.418).
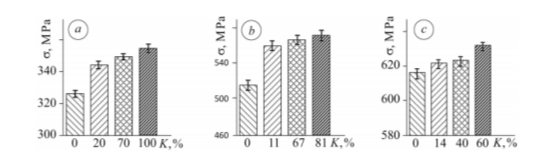
Determine 6. Energy in case of long run of speciments, (a) VT1-Zero , (b) PT-7M, (c)OT4-1 alloys, after the load for about 1000 hours with selection stage of floor hardening Okay (Fedirko et al.,2014, p.419, Determine 7).
Moreover, the research discovered that the hardening course of within the subsurface of a steel has an excellent affect on the efficiency of three of the alloys (PT-7M, OT4-1 and VT1-Zero) when subjected to long-term static load, as proven in Determine 6. The analysis indicated that when a specimen has been hardened to optimum ranges, the fracture stresses improve by as much as 10% after loading for 1000 hr, which makes the supplies resist and stand in opposition to destruction under long-term static hundreds. The research concluded that the sturdiness of the examined titanium alloys whose “subsurface layer is solid-solution-hardened to the optimum stage” will increase within the state of affairs of rotating bending and pure bending and 1000 hours of long-term static load in air, by 25%-35%, 10%-15%% and seven%-10% respectively. (Fedirko, et al.,2014, p.420).
It’s argued that the above research, although restricted to 4 varieties of titanium alloys, gives an perception into the advanced nature of understanding the hyperlink between manufacturing of metals, mechanical properties and behavior under long run static circumstances.
Koo et al., (2017) additionally carried out a research on the failure of metals under long run static hundreds, specializing in biodegradable metals, that are metals which have been developed utilizing steel alloys resembling iron, magnesium and zinc-based alloys. The aim of these alloys is to degrade progressively with time, while on the similar time offering mechanical power that’s required on the early stage of set up. Nonetheless the advanced physiological stresses induced by long run static loading make degradation unpredictable, thus posing a engineering problem for designers. It’s acknowledged that implantable units are subjected to excessive loadings largely on account of regular bodily actions and these loadings may end up in stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and fatigues on account of corrosion (CF). Nonetheless, Koo et al.,(2017) argue that in magnesium alloy-based biodegradable metals there may be larger stress that may trigger failure of the metallic medical system. It follows that there’s a want for an in depth research and analysis of how mechanical stress and corrosion have an effect on one another to doubtlessly make higher alloys. To this finish Koo et al.,(2017) carried out analysis how a long-term static stress affect magnesium alloys in phrases of degradation, investigating the induced adjustments in mechanical integrity. It’s famous that the analysis centered on supplies utilized in medical units, nevertheless it’s argued that such analysis has wider worth for the dialogue on the impacts of static loading on alloy metals.
On this analysis, Koo et al.,(2017) investigated magnesium alloys, ZE41A (T5) and AZ31B (H24) to guage stress corrosion cracking, as proven in Desk 1.
Desk 1 Stress Corrosion Cracking Check (Koo et al., 2017, p.46, Desk 1).
The analysis used EDX (vitality dispersive X-ray), micro CT (micro computed tomography) and SEM (scanning electron microscopy) to look at the microstructure of alloys and to characterise the floor morphology. To copy the static loading course of, the magnesium alloys had been subjected to a sequence of checks, summarised in Desk 2, together with a four-point bending check. Commonplace tensile checks had been additionally carried out and the yield power was calculated (Koo et al., 2017).
Desk 2. Tensile and Flexural Mechanical Exams (Koo et al., 2017, p.46, Desk 2).
The outcomes confirmed from four-point bending checks, displaying a lower of elastic modulus, yield power and flexural stress in addition to most power, as proven in Determine 7.
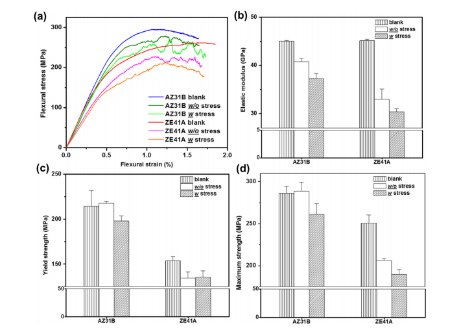
Determine 7. The outcomes of 4 level bending check: (a) Stress-strain curves, (b) Elastic modulus, (c) Yield power, (d) Most power of ZE41A and AZ31B. Clean = three, corroded alloys = 2 (Koo et al., 2017, p.52, Determine 9).
The analysis concluded that “long-term static loading can have an effect on degradation and mechanical integrity of Mg alloys under a careworn setting” (Koo et al., 2017, p.51). In different phrases, understanding of long-term static loading is essential for mechanical degradation course of.
Conclusion
This essay investigated the failure of metals under long run static hundreds. The analysis finds that failure depends on the sort of load, the time under which the fabric is subjected to that load and the mechanical properties of the steel. It’s evident from this research that the mechanical behaviour depends on the manufacturing of the steel, as every manufacturing course of induces stresses, strains and impurities within the materials which have an effect on the efficiency of that materials. It’s doable to foretell efficiency under variable imposed hundreds and static hundreds, nevertheless the latter may be advanced, on condition that the load circumstances and the setting inside which the fabric is positioned can differ with time, and situation. In brief while static hundreds can have an effect on failure, different components resembling corrosion can have an effect on the structural integrity of the steel which contributes to failure. It’s submitted that this research signifies that while there’s a important financial institution of analysis and understanding on typical metals, there’s much less analysis on the behaviour of alloys, regardless of the growing use of these supplies. The essay signifies that alloys are additionally affected by the tactic of manufacturing and the environmental circumstances.
References
- Andreikiv, O.E. and Sas, N.B., 2006. Fracture mechanics of metallic plates under the circumstances of high-temperature creep. Supplies Science, 42(2), pp.210-219.
- Bhaduri, A., 2018. Mechanical Properties and Working of Metals and Alloys. London: Springer Press.
- Ellobody, E., Feng, R. and Younger, B., 2014. Finite Component Assessment and Design of Metallic Buildings. Oxford: Elsevier.
- Forrest, P.G., 1970. Fatigue of Metals. Oxford: Elsevier.
- Fedirko, V.M., Luk’yanenko, O.H. and Trush, V.S., 2014. Affect of the diffusion saturation with oxygen on the sturdiness and long-term static power of titanium alloys. Supplies Science, 50(three), pp.415-420.
- Gere, J.M. and Goodno, B.J., 2012. Mechanics of Supplies. Cengage Studying.
- Harris, J.N., 2014. Mechanical Working of Metals: Principle and Observe. Oxford: Elsevier.
- Hosseini, S., Heidarpour, A., Collins, F. and Hutchinson, C.R., 2015. Impact of pressure ageing on the mechanical properties of partially broken structural gentle metal. Development and Constructing Supplies, 77, pp.83-93.
- Koo, Y., Jang, Y. and Yun, Y., 2017. A research of long-term static load on degradation and mechanical integrity of Mg alloys-based biodegradable metals. Supplies Science and Engineering: B, 219, pp.45-54.
- Lascoe, O.D., 1998. Handbook of Fabrication Processes. New York: ASM Worldwide.
- Lesiuk, G., Rymsza, B., Rabiega, J., Correia, J.A., De Jesus, A.M.P. and Calcada, R., 2019. Affect of loading course on the static and fatigue fracture properties of the long run operated metallic supplies. Engineering Failure Assessment, 96, pp.409-425.
- Macaulay, M., 2012. Introduction to Impression Engineering. London: Springer Science & Enterprise Media.
- Madia, M., Ngoula, D.T., Zerbst, U. and Beier, H.T., 2017. Approximation of the crack driving pressure for cracks at notches under static and cyclic loading. Procedia Structural Integrity, 5, pp.875-882.
- Martin, G. and Vladimír, C., 2017. Situations for Long-term Monitoring of Security in Operation of Pipelines. Procedia Structural Integrity, 5, pp.614-619.
- Matta, A.Okay., Kodali, S.P., Ivvala, J. and Kumar, P.J., 2018. Metallic Prototyping the longer term of Car Trade: A assessment. Supplies Immediately: Proceedings, 5(9), pp.17597-17601.
- McKown, S.S.S.S., Shen, Y., Brookes, W.Okay., Sutcliffe, C.J., Cantwell, W.J., Langdon, G.S., Nurick, G.N. and Theobald, M.D., 2008. The quasi-static and blast loading response of lattice buildings. Worldwide Journal of Impression Engineering, 35(eight), pp.795-810.
- Mišović, M., Tadić, N. and Lučić, D., 2016. Deformation traits of aluminium alloys, Gradevinar, 68(three), pp. 179-189.
- Nationwide Academy Press, 1995. Manufacturing Unit Processes. [online]. Out there at < https://www.nap.edu/read/4827/chapter/10 > [accessed 17th February 2019].
- Panin, S.V., Vlasov, I.V., Marushchak, P.O., Eremin, A.V., Byakov, A.V., Berto, F., Vinogradov, A.Y., Syromyatnikova, A.S. and Stankevich, R., 2017. Affect of long-term operation on construction, fatigue sturdiness and affect toughness of 09Mn2Si pipe metal. Procedia Structural Integrity, 5, pp.401-408.
- Wang, X.J., Xu, D.Okay., Wu, R.Z., Chen, X.B., Peng, Q.M., Jin, L., Xin, Y.C., Zhang, Z.Q., Liu, Y., Chen, X.H. and Chen, G., 2018. What’s going on in magnesium alloys?. Journal of Supplies Science & Know-how, 34(2), pp.245-247.
- Winzer, N., Atrens, A., Track, G., Ghali, E., Dietzel, W., Kainer, Okay.U., Hort, N. and Blawert, C., 2005. A essential assessment of the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of magnesium alloys. Superior Engineering Supplies, 7(eight), pp.659-693.
- Witte, F., 2010. The historical past of biodegradable magnesium implants: a assessment. Acta biomaterialia, 6(5), pp.1680-1692.
- Zerbst, U., Madia, M., Klinger, C., Bettge, D. and Murakami, Y., 2019. Defects as a root trigger of fatigue failure of metallic elements. III: Cavities, dents, corrosion pits, scratches. Engineering Failure Assessment, 97, 777-792.
